Differences between Invertebrate and vertebrate by Vania Almira
Definition:
Invertebrates
invertebrates are the most abundant organisms on earth. They occupy almost all habitats, they can be found crawling, flying, swimming or floating. Invertebrates are the animals without backbone. These animals do not have internal skeleton made of bone. They play a vital role in the earth's ecosystem. About 99 per cent of the known organisms are invertebrates. Out of the planets estimated 15-30 million species about 90% of the animals are invertebrates. These come in may shapes and sizes and provide services that are vital for our survival. The most common vertebrates include sponges, annelids, echinoderms, molluscs and arthropods. Arthropods includes insects, crustaceans and arachnids.
Animals of Invertebrates:
- Marine Invertebrates - There are a wide variety of interesting ocean animals that are invertebrates. These include sponges, corals, jellyfish, anemones, and starfish.
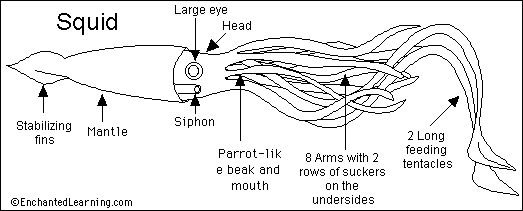
- Mollusks - Mollusks have a soft body that is covered by an outer layer called a mantle. Many mollusks live inside a shell, but not all of them. Some examples of mollusks include squid, snails, slugs, octopuses, and oysters.
- Crustaceans - Crustaceans are a type of arthropod, meaning that they have jointed legs. They also have an exoskeleton (their bones are on the outside like a shell). Some examples of crustaceans are crabs, lobster, shrimp, and barnacles.
- Worms - The term "worm" is not a scientific word, but is often used to refer to invertebrate animals that don't have legs. Worms may live in the soil, in the water, or even inside other animals as parasites. Some examples include the tapeworm, the leech, and the earthworm.
- Insects - Insects are part of the Earth's largest animal phylum, the arthropods. There are over 1 million species of insects including such animals as the grasshopper, dragonfly, yellow jacket, butterfly, and praying mantis.
- Spiders, Centipedes and Scorpions - These animals are all part of the arthropod phylum. Spiders and scorpions are arachnids because they have eight legs. Centipedes and millipedes are myriapods and have lots of legs. Some myriapods have as many as 750 legs. Some example species include the tarantula and black widow, which are both spiders.
Vertebrates:
Vertebrates are animals that have a backbone or spinal column, also called vertebrae. These animals include fish, birds, mammals, amphibians, and reptiles. Vertebrates are classified by the chordate subphylum vertebrata. Invertebrates are any other animal that is classified outside of that class. There are currently around 65,000 known species of vertebrate animals. This sounds like a lot, but vertebrates are only around 3% of all the animals on Earth. Most of the animal species are invertebrates.
Animals of Vertebrates:
- Fish - Fish are animals that live in the water. They have gills that allow them to breathe under water. Different species of fish may live in fresh water or salt water. Some examples of fish include the brook trout, the great white shark, lionfish, and the swordfish.
- Birds - Birds are animals that have feathers, wings, and lay eggs. Many, but not all, birds can fly. Some examples of bird species include the bald eagle, the cardinal, the flamingo, ostriches, and the red-tailed hawk.
- Mammals - Mammals are warm-blooded animals that nurse their young with milk and have fur or hair. Some examples of mammals include humans, dolphins, giraffes, horses, and spotted hyenas.
- Amphibians - Amphibians are cold-blooded animals. They start out their lives living in the water with gills just like fish. Later they develop lungs and can move to dry land. Amphibians include frogs, toads, newts, and salamanders.
- Reptiles - Reptiles are cold-blooded animals which lay eggs. Their skin is covered with hard and dry scales. Reptile species include alligators, crocodiles, snakes, lizards, and turtles.
Differences:
• Vertebrates have a backbone with a spinal cord, whereas invertebrates do not.
• The diversity is exceptionally high among the invertebrates compared to vertebrates.
• Vertebrates are always bilaterally symmetrical, while invertebrates could show either bilateral or radial symmetry.
• Vertebrates are usually large-bodied and move fast compared to invertebrates.
• Vertebrates have a closed blood system, a well-developed brain, either gills or lungs for respiration, and a complex and sophisticated nervous system, whereas those are primitive in invertebrates. Therefore, it concerns that vertebrates have many specializations to extract the best out of the environment compared to invertebrates.
From those differences above, someone could has an additional infromation that invertebrates are more adaptive due to their simplicity, whereas vertebrates do not have a good adaptability in comparison because of the specialization. However, I would like to quote a popular quote to finish that in evolution specialization paralyses and ultra specialization kills the viability of taxons.
Characteristics of Invertebrates
- The main characteristic that separates invertebrates from other organisms is the absence of the spinal column and backbone.
- They are multicelluar organisms, they completely lack cell walls.
- They are devoid hard bony endoskeleton.
- Due to the lack of complex skeletal systems, some invertebrates tend to be slow and small in nature.
- Due to the lack of the backbone and complex nervous system the invertebrates cannot occupy mulitple environments, though they are found in the harshest of the environments.
- Invertebrates live all over the world in various habitats.
- Body is divided into three parts - head, thorax and the abdomen.
- They do not have lungs for respiration.
- Respiration is through skin.
- Some invertebrate groups possess a hard, chitinous exoskeleton.
- Most of them have tissues, that are specific organization of cells.
- Most of them reproduce sexually by the fusion of the male and female gametes.
- Few invertebrates like the sponges are sedentary, but most of the organisms are motile.
- Most invertebrates are organized with symmetric body organization.
- They can not make their own food, are heterotrophs.
( Post by Vania Almira )